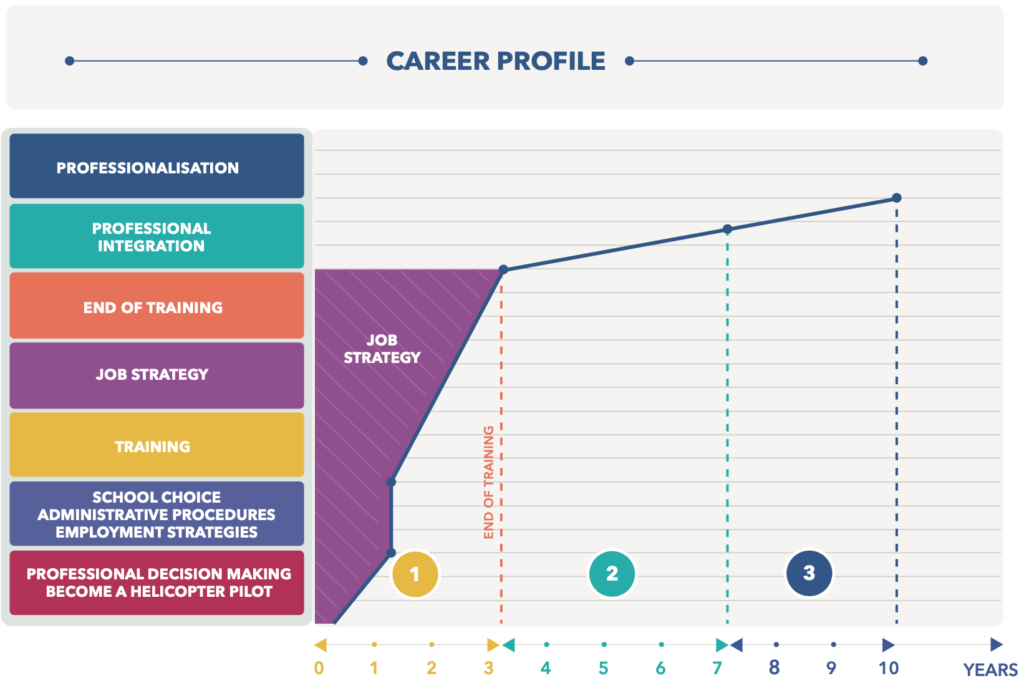
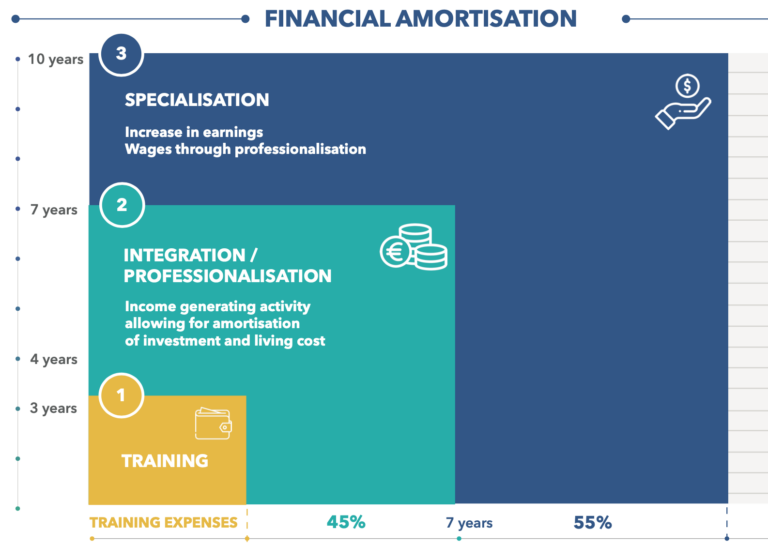
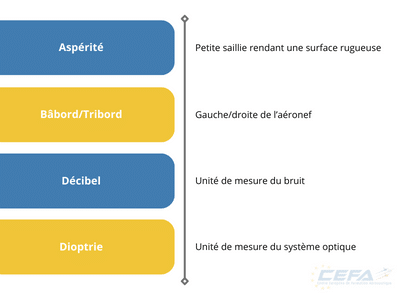
Aviation is a fascinating field, rich with terminology and procedures essential for ensuring the safety and efficiency of flights. Among the most commonly used terms are IFR and VFR. But what do these acronyms mean, and what are their fundamental differences? This article explores the characteristics of each type of flight to help you better understand these key concepts.
What is the Difference Between IFR and VFR?
IFR: Instrument Flight Rules
IFR, or Instrument Flight Rules, is a set of aviation regulations that allow pilots to fly an aircraft using only the onboard instruments, without any visual reference to the outside environment. This type of flight is particularly useful and often necessary in weather conditions where visibility is reduced, such as in thick clouds, fog, or during night flights.
Advantages of IFR:
- Increased Safety: Onboard instruments enable precise and reliable navigation, even in the absence of external visual references. Pilots can safely fly in challenging weather conditions.
- Flexibility: IFR flights can be conducted in a variety of weather conditions, providing greater flexibility in flight planning. Pilots are not limited by the need for good visibility.
- Air Traffic Control: IFR pilots are in constant contact with air traffic controllers, allowing for more organized and secure management of airspace. This reduces the risk of collision and improves coordination between aircraft.


Disadvantages of IFR:
- Complexity: Training to obtain IFR certification is more intensive and complex than for VFR. It requires a thorough understanding of onboard instruments, navigation procedures, and air traffic rules.
- Cost: The equipment needed for IFR flights is generally more expensive, as it includes advanced navigation instruments and sophisticated communication systems.
Requirements for IFR Flight:
To fly under IFR, a pilot must obtain specific certification, which includes comprehensive training in instrument navigation, meteorology, and IFR flight procedures. Aircraft must also be adequately equipped to meet IFR requirements, including appropriate navigation and communication instruments.
VFR: Visual Flight Rules
VFR, or Visual Flight Rules, relies on the pilot’s ability to navigate based on external visual references, such as the horizon, terrain, and landmarks. VFR flights are typically conducted in good weather when visibility conditions are favorable.
Advantages of VFR:
- Simplicity: VFR rules are simpler and quicker to learn, making them an ideal first step for beginner pilots. VFR training focuses on the basic principles of flight and visual navigation.
- Reduced Cost: Less equipment is needed for VFR flights, which can lower operating and maintenance costs for aircraft.
- Flight Experience: VFR pilots can enjoy panoramic views and a more enjoyable flight experience, with the ability to directly observe the landscape and visual landmarks.


Disadvantages of VFR:
- Weather Limitations: VFR flights are limited by weather conditions, requiring good visibility and the absence of low clouds. VFR pilots often need to adjust or delay their flight plans based on weather conditions.
- Less Flexibility: Due to weather restrictions, VFR pilots have less flexibility in flight planning. They must ensure that weather conditions remain favorable throughout the flight.
Requirements for VFR Flight:
To fly under VFR, a pilot must hold a valid pilot’s license and comply with specific air traffic rules for VFR flights. Aircraft must be appropriately equipped for VFR flight, though the equipment requirements are less stringent than for IFR flights.
Choosing Between IFR and VFR
The choice between IFR and VFR depends on several factors, including the pilot’s experience, weather conditions, route complexity, and specific flight requirements. Here are some considerations to help make this choice:
- Beginner pilots generally start by learning VFR rules, as they are simpler and allow familiarization with the basics of flight.
- Experienced pilots, who wish to fly in various weather conditions and over longer distances, may choose to obtain IFR certification.
- IFR flights are preferred in difficult or unpredictable weather conditions, as they allow safe navigation using onboard instruments.
- VFR flights are ideal in good weather, with good visibility and stable weather conditions.
- IFR flights are often used for complex routes, requiring precise navigation and coordination with air traffic control.
- VFR flights are better suited for simple routes, with clear visual landmarks and direct navigation.
- For commercial flights or flights in controlled airspace, IFR is often mandatory to ensure safety and coordination with other aircraft.
- For leisure flights or local flights, VFR offers a pleasant and flexible flying experience.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between IFR and VFR is crucial for any pilot or aviation enthusiast. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice largely depends on the specific circumstances of the flight and the pilot’s skills. At CEFA, we offer comprehensive training for both types of flights, enabling our students to become versatile and competent pilots.
For more information on our training programs and to find out which one is right for you, please contact us.